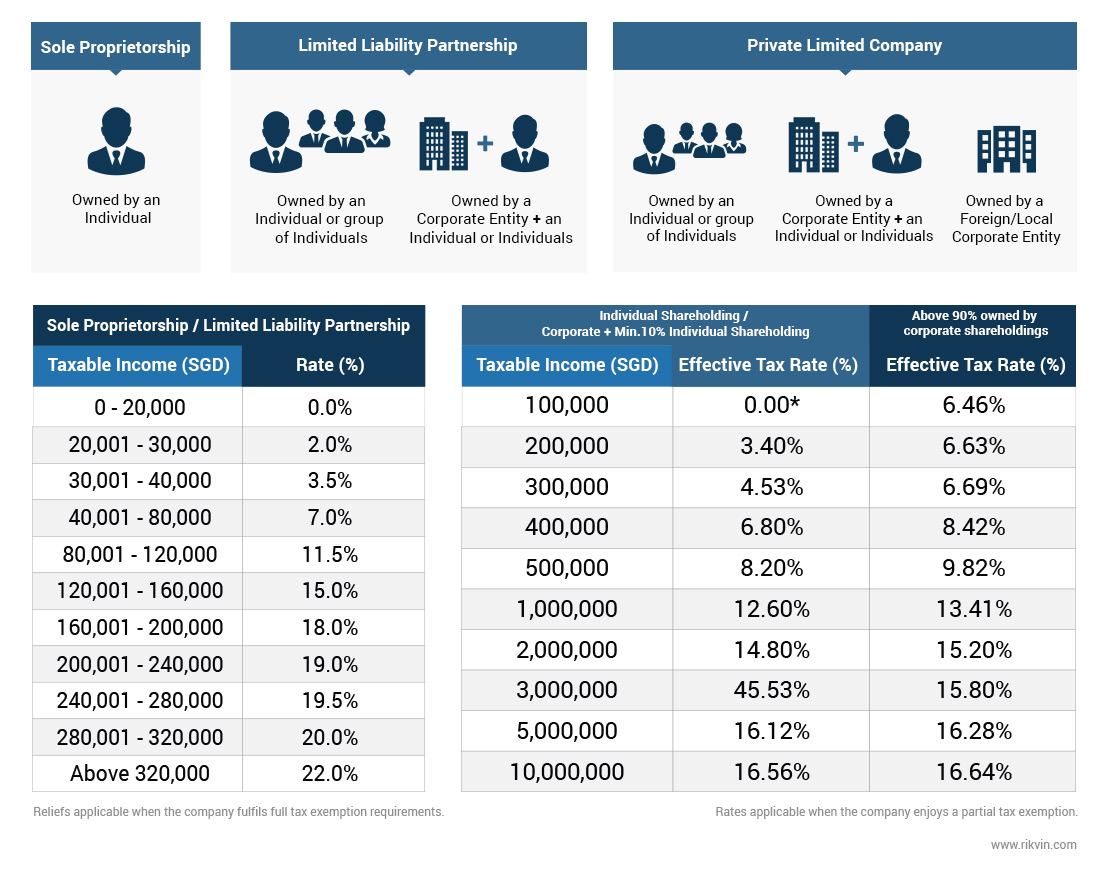
Comparison Chart for Singapore Residents
This guide provides a side-by-side comparison of the different types of business entities in Singapore, namely, Sole Proprietorship, Limited Liability Partnership, and Private Limited Company.
| Types of Companies Structure | Sole Proprietorship | Limited Liability Partnership | Private Limited Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suitable For | Individual with low risk | Professional firms such as accountancy, law and architecture. | For businesses with projected growth, which may require additional funding for expansion. |
| Advantages | Low cost Business setup |
Low cost setup with limited liability protection | Tax exemptions For new exempt companies only: taxed at the corporate rate; first S$100,000 of net income each year is tax free and the next S$200.000 taxed at 8.5% for the first 3 years. |
| Disadvantages | Personal Assets Not Protected | None | Compliance obligations such as Financial Reports, AGMs, etc |
| Ownership |
|
|
|
| Separate Legal Entity | No | Yes | Yes |
| Cap on Number of Members | One | Unlimited | Maximum 20 for exempt companies |
| Minimum Setup Requirement | One owner | 2 partners | 1 shareholder and 1 director (the same individual can be both) |
| Limited Liability | No | Yes | Yes |
| Accounts Audit | No | No | Yes, for turnover above S$5 Million or non-exempt companies |
| Tax Treatment | Taxed at personal income tax rate | Taxed at personal income tax rate | Dividends are tax exempt |
| Cessation of Business upon Death of a Member/Partner | Yes | Yes | No. Equity shares go on in perpetuity. |