Singapore Subsidiary Company Registration
Imagine your business flourishing in the heart of Southeast Asia. Setting up a Subsidiary Company in Singapore opens doors to exciting opportunities, and this guide will equip you with everything you need to make it a reality.
How to Register a Singapore Subsidiary Company?
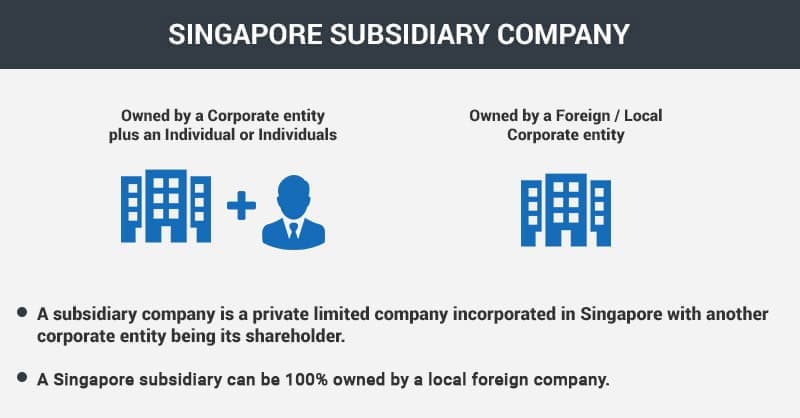
A Singapore subsidiary is a private limited company incorporated in Singapore in which the majority shareholder is a foreign or a local company. It has a legal identity distinct from the parent company’s.
This page provides a detailed overview of a Singapore subsidiary company registration process. A properly structured subsidiary company is a very tax-efficient corporate body; hence, this form is the most common type of entity registered in Singapore by foreign companies.
A Singapore subsidiary is the most preferred choice for foreign companies to establish their presence in Singapore. Singapore allows 100% foreign shareholding. The shareholder’s liability is limited to the value of the shares it subscribes to. Singapore does not restrict the repatriation of any profit or capital of a Singapore subsidiary.
A Singapore subsidiary, wholly owned by a foreign company, is recognised as a distinct legal entity apart from its parent company. The liability of the parent company is restricted solely to the subscribed share capital, thus safeguarding its assets from the debts and obligations of the subsidiary.
Additionally, a Singapore subsidiary is typically treated as a local resident company, thereby qualifying for tax incentives accessible to local entities.
The Incorporation of a Singapore Subsidiary Company comes into existence upon registration under the Companies Act (Cap 50) with the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA). A Singapore subsidiary company is also considered a resident company for tax purposes.
What Are the Singapore Subsidiary Registration Requirements?
-
Proposed Name of Subsidiary
Before the Singapore Company can be incorporated, ACRA must approve the company name. If a proposed company name is similar to another existing company name, or unacceptable or identical to names reserved by the Minister in its registry, ACRA will refuse it for incorporation.
Check your Singapore company name availability »
-
Shareholders
It is necessary to have at least one corporate shareholder. A director and a shareholder may or may not be the same person (s). 100% local or foreign corporate shareholding is allowed. A Singapore Private Limited Company can have a minimum of one and a maximum of 50 shareholders, according to the Singapore Companies Act. The names and addresses of shareholders would be made public.
Frequently asked questions: Who is a Shareholder? »
-
Resident Directors
A Singapore Private Limited Company must have at least one director who must be an “ordinary” resident in Singapore, i.e. a Singapore citizen, a Singapore permanent resident, or a person who holds an Employment Pass/EntrePass or a Dependant Pass with a residential address in Singapore.
There is no limitation on the number of additional local or foreign directors a Singapore Private Limited Company can appoint. The director must be at least 18 years of age, and must not be bankrupt or convicted of any criminal malpractice in the past. Information about the directors will appear on public records. Directors can also be shareholders or vice versa.
-
Company Secretary
The company secretary must be a natural person who is an “ordinary” resident in Singapore. The Singapore Companies Act requires each company to appoint a company secretary within six months of incorporation.
-
Share Capital/Paid-up Capital
The minimum paid-up capital for the registration of a Singapore company is S$1 or its equivalent in any other currency. The parent company may own 100% of the company’s shares. There is no concept of authorized capital in Singapore.
-
Registered Address
Every company registered in Singapore is required to have a registered office address. The registered address must be a physical address and cannot be a PO Box. The use of the residential address is allowed for certain types of business.
-
Governance Structure
The governance structure of a company and the interrelationship between the company and its shareholders are governed by the company’s. It is also not uncommon to find the members of companies (usually in joint venture arrangements) entering into ‘shareholder agreements’ among themselves to capture some of their key rights and obligations about how the company is to be structured and managed.
-
Auditor
After the Singapore subsidiary is registered, an auditor must be appointed within three months.
-
Audited Accounts
A Singapore subsidiary must file audited accounts annually. However, dormant companies may file unaudited financial reports.
What Are the Audit Exemption Criteria for a Singapore Subsidiary Company?
All subsidiary companies must file an audit report unless it meets the new Audit Exemption criteria for a “small group”. For a group to be a “small group”, the parent and the subsidiary company must meet at least 2 of the 3 quantitative criteria on a consolidated basis:
- Aggregate turnover must be not more than SGD $10 million
- The aggregate balance sheet total must be not more than SGD $10 million at the end of the financial reporting period
- The number of employees at the end of each financial year does not exceed 50
What Are the Tax incentives for Subsidiary Company?
Subsidiary companies incorporated in Singapore can take advantage of the republic’s extensive network of Free Trade Agreements (FTA) and Avoidance of Double Tax Agreements (DTAs).
If the company has at least one individual shareholder holding with at least 10% shares of the subsidiary company, the firm is entitled to zero tax on the first S$100,000 of chargeable income for the first 3 consecutive years.
Procedure and Timeline for Singapore Subsidiary Registration
Registering a Singapore subsidiary company is a dynamic process that is conducted online. Foreign companies must appoint a professional corporate services firm to set up an entity in Singapore. The registration can be completed in just a few hours, provided that all documents are in order. Registration procedure for Singapore subsidiary is as follows:
| Procedure | Responsibility | Average Timeline | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fill up our online form to get started with the Singapore Subsidiary Company incorporation process. | Client | 10 minutes |
The following documents are required for the registration of a Singapore Subsidiary:
Note: All documents must be in English and any non-English documents must be translated into English. |
Client | Depends on you | |
| Upon completion of the above, we will | |||
| 1 | Reserve Subsidiary company name | Rikvin | 10 minutes |
| 2 | Prepare necessary incorporation documents | Rikvin | 30 minutes |
| 3 | Sign and return incorporation documents | Client | Depends on you |
| Upon completion of the above, we will | |||
| 1 | Incorporate the company with the Accounting & Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) of Singapore | Rikvin | 20 minutes |
| 2 | Prepare company documents for bank account opening and handover to the client | Rikvin | 15 minutes |
What Are the Singapore Work Visa Options for Subsidiary Companies?
- If you plan to relocate your management and key employees to Singapore to run their newly setup Singapore subsidiary, we can help you with your EP application.
- Foreign corporations that do not intend to relocate to Singapore to operate the company must appoint a Singapore resident director per the Singapore Companies Act.
Recommended for you What you need to know about Singapore Employment Pass »
How to Open a Singapore Corporate Bank Account?
Once the subsidiary company has been incorporated, you may open a corporate bank account with any of the local or international banks based in Singapore.
If you are unable to come to Singapore, you may choose a bank that allows the opening of a corporate bank account without your physical presence subject to bank “KYC” ( know your client) due diligence policies.
Frequently asked a question about Opening a Corporate Bank Account in Singapore »
Post Registration and Compliance
-
Licenses and Permits
Some business activities in Singapore are subject to regulation by government authorities. Even if your business firm has been registered you cannot begin operations unless you have the necessary approval or license from the relevant government authorities.
Private schools, video companies, travel agencies, liquor distributors, money lenders, banks, financial advisers, childcare centers and importers, wholesalers, and retailers of liquor licenses are some examples of businesses that need permits to operate.
-
Registered Office Hours
You must have a registered office address and the office must be open to the public for at least 3 hours per day on weekdays during normal business hours.
-
Registration Number
The business registration number issued by ACRA must be included on all letterheads, invoices, billings, or other documents used for official business communications.
-
Customs Registration
If your business activities involve import, export, and transshipment in and out of Singapore, you will need to register your company with the Singapore Customs and obtain a CR Number commonly known as Custom Registration. The central registration number is mandatory for Singapore companies or organisations engaged in trading activities.
-
Singapore Goods and Services Tax Registration
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a tax on the supply of goods and services in Singapore and the import of goods into Singapore. Goods exported from Singapore and international services provided from Singapore are exempt from GST. The current rate is 9% (w.e.f. 1st January 2024).
If your annual taxable revenue is more than S$1 million, or you are currently making taxable supplies, and your annual taxable revenue is estimated to be more than S$1 million, you must apply for GST. The company must file for GST within thirty days of becoming liable.
You may also opt to register for GST on your own. The Comptroller in IRAS has the authority to approve voluntary registration. You must register for at least two years after gaining approval.
-
Singapore Central Provident Fund (CPF) Registration
The CPF is a mandatory pension fund to which both the employer and the employee contribute a portion of their monthly salary. Employer CPF contributions are required for all local employees who earn more than S$500 per month and are Singapore citizens or permanent residents. Employer and employee CPF contribution rates are capped at 17% and 20%, respectively, and can be lower based on employee age, permanent resident status, and other factors. Foreign workers are not expected to contribute to the CPF.
All work passes employees need not contribute to the CPF.
- Trademark Registration:
While registering your business with ACRA is crucial, it doesn’t automatically protect your brand identity. To legally safeguard your brand name, logo, or slogan, you need to register it as a trademark with the Intellectual Property Office of Singapore (IPOS). This exclusive right allows you to prevent others from using similar or identical marks that might mislead consumers.
Ongoing Singapore Company Compliance Considerations
Once your Singapore Subsidiary Company is incorporated, you must comply with the statutory requirements set by the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) and Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS).
People also ask
- A Singapore subsidiary is a private limited company in which the majority shareholder is a foreign or local company. It is also considered a legal identity separate from the parent company’s.
To start a subsidiary in Singapore, you will require the following:
Proposed name of the subsidiary
Minimum 1 shareholder
Minimum 1 resident director
Local company secretary
Local registered address
Minimum S$1 paid-up capital
Governance structure
Memorandum & Articles of Association
Auditor (should be appointed within 3 months of subsidiary registration)
Audited accounts- Yes, as long as your subsidiary is incorporated in Singapore, you are eligible for tax incentives and can tap into the Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and Avoidance of Double Tax Agreements (DTAs).
- Yes, in Singapore, 100% foreign shareholding is allowed.
- In the case of a subsidiary, it is required that the foreign parent or holding company possesses a minimum of 50% ownership in shares. This implies that the parent’s share ownership should fall within the range of 50% to 99%.
- Startups are not eligible for recognition as holding or subsidiary companies. If a startup undergoes a transformation into a holding or subsidiary entity after receiving recognition, it will be subject to derecognition.
Form a Singapore subsidiary company today
An hour is all we need. Coupled with transparent, highly-competitive pricing and timely, committed support, your subsidiary company registration is made easy.