A Personal Income Tax Guide for Foreigners in Singapore

Living and working in Singapore has many benefits. You can pamper yourself with the best place in Southeast Asia to live, work and play, and enjoy the other great nations of the region.
Some examples are Vietnam, Cambodia, Malaysia, Thailand, and Indonesia, which are all not more than a two-hour flight away from Singapore’s world-class Changi Airport.
The Lion City also offers other perks, such as a favourable tax and business environment. With one of the lowest tax rates in the world, here’s an overview of the personal income tax guide in Singapore.
In this guide, we present the personal income tax rates for tax-resident foreigners in Singapore, as well as the various rebates and reliefs to that they are entitled to.
In general, the Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS), Singapore’s tax regulator, treats non-Singaporeans and non-Singapore Permanent Residents as foreigners for tax purposes.
Such individuals, depending on their tax-residency status, are liable to income tax on all income derived from or accrued in Singapore. This article covers the following points :
- Tax-residency of Foreigners in Singapore
- Singapore Personal Tax rates
- Not Ordinarily Resident Scheme
- Tax Filing Dates in Singapore
- Income Tax Reliefs for Tax Residents* in Singapore
Tax-residency of Foreigners in Singapore
 The Singapore tax rate which a foreigner pays depends on the tax-residency status, with the cut-off periods being 60 days and 183 days. Let’s understand this in detail.
The Singapore tax rate which a foreigner pays depends on the tax-residency status, with the cut-off periods being 60 days and 183 days. Let’s understand this in detail.
Related Read: Singapore Personal Tax for Non-Residents
At Least 183 Days
Under the city-state’s tax residency rules, a foreigner is regarded as a tax resident if he or she stays or works in Singapore for at least 183 days in a calendar year.
Notably, the number of counted days includes weekends and public holidays, and any temporary absence from work for overseas vacation or official work.
So the tax implications will be:
| Period of stay (including work) in Singapore | Tax-resident status | Tax liability |
|---|---|---|
| At least 183 days in a year | Yes | Income taxed at progressive resident rates |
| At least 183 days for a continuous period over two years | Yes | Income taxed at progressive resident rates |
| At least 183 days for a continuous period over three consecutive years | Yes | Income taxed at progressive resident rates |
While the foreigner can claim tax reliefs (discussed below) when filing the Form B1 applicable to tax residents, his or her foreign-sourced income brought into Singapore is tax-exempt.
Do note that according to the rules, a foreigner who stays or works in Singapore continuously for three consecutive years, he or she is regarded as a tax resident for all three years even if the number of days in Singapore is less than 183 days in the first and third year.
The progressive resident rates range from zero to 22% with the topmost rates kicking in at S$320,000 annual income as detailed below.
Singapore Income Tax Rates
| INDIVIDUAL TAX RATES OF TAX (From YA 2017 to YA 2023) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chargeable Income | Income Tax Rate (%) | Gross Tax Payable ($) | |
| On the first On the next |
20,000 10,000 |
0 2 |
0 200 |
| On the first On the next |
30,000 10,000 |
– 3.5 |
200 350 |
| On the first On the next |
40,000 40,000 |
– 7 |
550 2,800 |
| On the first On the next |
80,000 40,000 |
– 11.5 |
3,350 4,600 |
| On the first On the next |
120,000 40,000 |
– 15 |
7,950 6,000 |
| On the first On the next |
160,000 40,000 |
– 18 |
13,950 7,200 |
| On the first On the next |
200,000 40,000 |
– 19 |
21,150 7,600 |
| On the first On the next |
240,000 40,000 |
– 19.5 |
28,750 7,800 |
| On the first On the next |
280,000 40,000 |
– 20 |
36,550 8,000 |
| On the first In excess of |
320,000 320,000 |
– 22 |
44,550 |
What is the Not Ordinarily Resident Scheme?
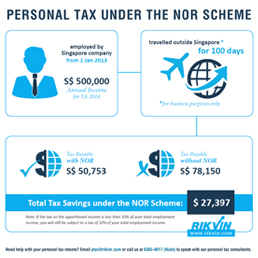 In Singapore, a special category of individuals called the Not Ordinarily Residents (NOR) are given favourable tax treatment for a period of five years of assessment.
In Singapore, a special category of individuals called the Not Ordinarily Residents (NOR) are given favourable tax treatment for a period of five years of assessment.
To be eligible, an individual must be:
- A non-resident in Singapore for tax purposes in the past three years of assessment; and
- In that year of assessment in which the individual qualified for the NOR status, he or she must have been a Singapore tax-resident
Importantly, to retain a NOR taxpayer status, the foreigner is only required to be a tax resident in the first year of assessment, and not throughout the 5-year qualifying period.
Benefits of the Not Ordinarily Resident Scheme
- A NOR taxpayer pays income tax on only that part of his employment income that corresponds with the number of days he spends in Singapore provided he had spent at least 90 days outside Singapore for business reasons and has got at least $160,000 as total Singapore employment income.
- A NOR taxpayer gets to enjoy tax exemption on contributions made by the employer to a non-mandatory overseas pension fund which would otherwise be taxable in his hands.
Less Than 183 Days
 As is self-evident, a foreigner is a non-resident for tax purposes if his or her stay in Singapore is less than 183 days in a calendar year. For such individuals:
As is self-evident, a foreigner is a non-resident for tax purposes if his or her stay in Singapore is less than 183 days in a calendar year. For such individuals:
No tax reliefs are given when filing Form M applicable to non-residents but only the income earned in Singapore is taxed at a flat rate of 15% (or at progressive resident rates, if it gives a higher tax liability). Notably, Director’s fees are taxed at a slightly higher rate of a flat 20%.
Less Than or Equal to 60 Days
For foreigners who are in Singapore for less than or equal to 60 days, IRAS doesn’t charge any taxes and treats them as non-residents too.
Do note that this exemption does not apply to directors of a company, public entertainers, foreign experts, foreign speakers, queen’s counsels, consultants, trainers, coaches, etc. (i.e. all these come under the category of “professionals”).
Filing Date in Singapore
 IRAS mandates that all tax returns must be filed (with completed paper tax forms) by April 15 every year. If individuals are using the IRAS e-filing portal, this deadline is extended to three more days i.e. April 18.
IRAS mandates that all tax returns must be filed (with completed paper tax forms) by April 15 every year. If individuals are using the IRAS e-filing portal, this deadline is extended to three more days i.e. April 18.
In exceptional circumstances, the filing date may be extended too. But for that the requisite application must be sent to IRAS by March 31, detailing the reasons for the desired extension, full name, tax reference number, and an estimate of the chargeable income.
Do note that sometimes IRAS may waive the requirement to file an income tax return for taxpayers who only have Auto-Inclusion Scheme (AIS) for employment income and their relief claims are the same as the previous year.
Income Tax Reliefs for Tax Residents* in Singapore
*either local or foreign tax-resident
Even though the progressive rates for personal income tax rates range from zero to 22% in Singapore, the effective payable tax may come out to be much lower if one takes advantage of the various schemes the Singapore Government has initiated. These include reliefs on earned income; spouse, child, and parent-support; reliefs on life insurance policies, course fees, and foreign maid levy; and the relief given on Supplementary Retirement Scheme (SRS). Below we detail the qualifying conditions and the amount of tax relief given on each.
Read more on how to reduce tax in Singapore.
FAQs
- Yes, but your tax liability will depend on your tax residency status. This is important as it determines the amount of taxes a foreigner pays in Singapore, with the cut-off periods being 60 days and 183 days. For example, if you are issued with a work pass that is valid for at least one year, you will be treated as a Singapore tax resident upfront. So, a foreigner is a non-resident for tax purposes if his or her stay in Singapore is less than 183 days in a calendar year. For such individuals, no tax reliefs are given when filing Form M applicable to non-residents but only the income earned in Singapore is taxed at a flat rate of 15% (or at progressive resident rates, if it gives a higher tax liability). For foreigners who are in Singapore for less than or equal to 60 days, IRAS doesn’t charge any taxes and treats them as non-residents too.
- For Foreigners working in Singapore, the following conditions are also applicable for the taxability of their income in Singapore:
- If you work in Singapore for 60 days or less in a calendar year, you will be exempt from tax on your earnings here. This exemption does not apply to non-resident company directors, public entertainers, professionals including foreign experts, speakers, queen’s counsels, consultants, trainers, coaches, etc.
- If you stay or work in Singapore for 61 to 182 days in a calendar year, your income will be taxed at 15% or resident rates for individuals, whichever gives the higher tax.
- If you stay or work in Singapore for 183 days or more in a calendar year, your income will be taxed at resident rates for individuals.
- If you stay or work in Singapore for a continuous period of at least 183 days over two years, your income will be taxed at resident rates for individuals.
- If you stay or work in Singapore for three consecutive years, your income for all years will be taxed at resident rates.
- For overseas income which is taxable, you have to declare the income under ’employment income’ (if your employer is not under the AIS)*, ‘trade income’ or ‘other income’ (whichever is applicable) in your tax return. This can be done via e-filing at myTax Portal, mobile phone, or using a paper form. Under the Auto-Inclusion Scheme (AIS), employers submit the employment income information of their employees to IRAS electronically. The submitted information will then be automatically included in the employees’ income tax assessment. Notably, we provide these services as part of our corporate secretarial services to ease your compliance burden.
How to Estimate Your Payable Personal Income Tax
Use our Online Income Tax Calculator to estimate your payable personal income tax for the current Year of Assessment.

